This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy
Digital Nation: Stronger Economy, Better Society and Adept Governance

Nations around the world are increasingly aware of the importance of digitalization. Many countries are embracing a vision to build a Digital Nation with enhanced economic vitality, robust social safety nets, and efficient and fair governance. The success of Digital Nation initiatives depends heavily on having anopen environment, especially the application of borderless technology, which means applying universal borderless technology, and promoting the appropriate integration of international and local partners. When done correctly, Digital Nation becomes a part of the fabric of an economy, society and governance, and relies on technological capabilities and supporting policies.
Our research shows that the economy and society transform alongside ongoing digitalization. According to the report published by Huawei and Oxford Economics, digitalization will produce a sustaining effect on the economy (i.e., "digital spillover”). Specifically, for every one US dollar invested in digital, GDP will grow by 20 dollars. Digitalization will also facilitate the fulfillment of the UN's SDGs.
Digitalization promotes an increase to economic efficiency in all industries, through the creation of new business models. In the finance, traditional enterprises apply new digital technologies to enhance their competitive advantages. The convergence of finance and technology is also resulting in the emergence of a new wave of FinTech enterprises. In the transportation, digitalization has led to the new business model of ride sharing. At the same time, an Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) can effectively increase carrying capacity and speed, and lower the failure rate of infrastructure. In the energy, smart grid technology is helping to optimize power generation, transmission, transformation, storage, distribution, and consumption.
In manufacturing, traditional manufacturers are upgrading by digitalizing technological processes, with many new product technologies emerging as a result. In the social sphere, digitalization optimizes resource allocation and improves lives. Globally, intelligent health risk prevention, public medical resources sharing, facilitation of professional training, and collaborative operation of medical facilities will solve key pain points in the healthcare field. Other applications such as remote education, customized content, and virtual classrooms have gradually matured, and are alleviating difficulties previously faced in education.
In respect to governance, digitalization could improve government efficiency and urban administration. Digitalization will assist in the realization of interactive policy channels, self-service transactions, integrated data management, and reliable information encryption in order to improve government services. Digitalization will also boost the formation of a new-era urban management system with self-adaptive environmental protection, independent emergency response, self-verifiable food traceability, and autonomous municipal regulations.
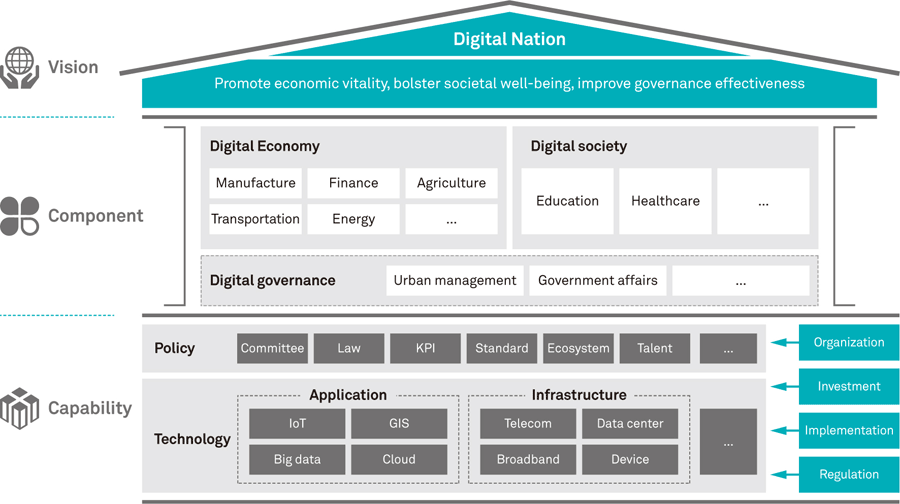
Every nation will encounter some form of difficulties and challenges during the process of digitalization, including ambiguity about who should organize and implement the initiatives, insufficient supporting resources, inadequate societal participation, a lack of flexible response to change, and lack of unified standards. Therefore, we suggest that governments take proactive measures such as organization, investment, implementation, and regulations, to effectively act as practitioners, motivators, and regulators in digitalization. Specific measures include building a top-down and integrated digital department, establishing a vertical organization specialized in key areas, expanding sources of funding, investing in ICT infrastructure, attracting and training digital talent, forming internal technical foundations, providing open access to public governmental database, implementing digital applications for e-Government, cultivating a digital ecosystem, developing global standards, establishing evaluation indicators, and ensuring data security and privacy, as well as encouraging the exchange of data.

