Academies and Academia: Developing Talent for the Intelligent Future
"If you are planning for a year, sow rice; if you are planning for a decade, plant trees; if you are planning for a lifetime, educate people," so states the ancient Chinese philosopher Guan Zhong about the importance of developing talent in his book Cultivation of Authority. According to another Chinese classic, History of Song, "The good governance of a country lies in talent, and the creation of a country's talent lies in education."
Huawei understands the importance of talent and is committed to collaborating with universities and colleges to foster an ecosystem for training teachers and students. Doing so will improve higher education, help train high-quality ICT talent, and accelerate the intelligent transformation of industries.
ICT talent enables the intelligent transformation of industries
Intelligent transformation has become a global trend in which ICT talent will play a key role by applying new mindsets and technologies to facilitate industry development and a sustainable digital economy.
Collaboration between enterprises and universities is a key aspect of developing talent. The rapid development of intelligent digital technologies requires that teaching and internships keep pace with industry trends. By combining the skills that enterprises need and their successful practices into education, collaboration can improve the quality of talent training to prepare students for industry development while supporting enterprise research and innovation.
Universities, enterprise, and students all benefit.
Huawei collaborates with universities to drive high-quality education
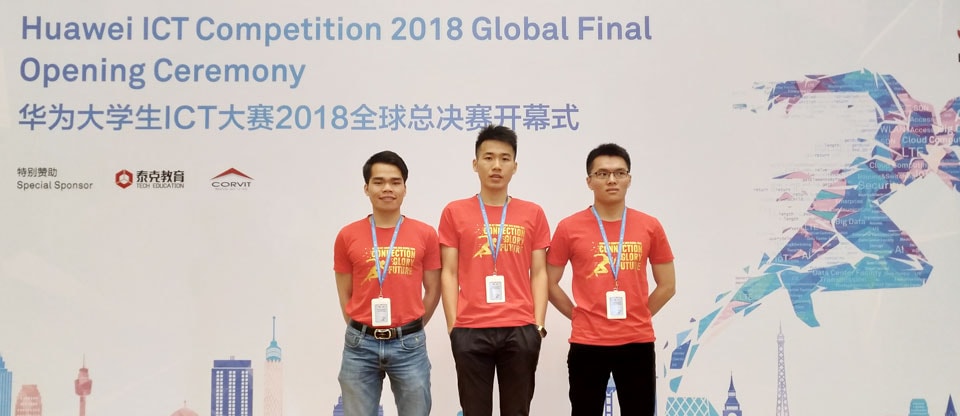
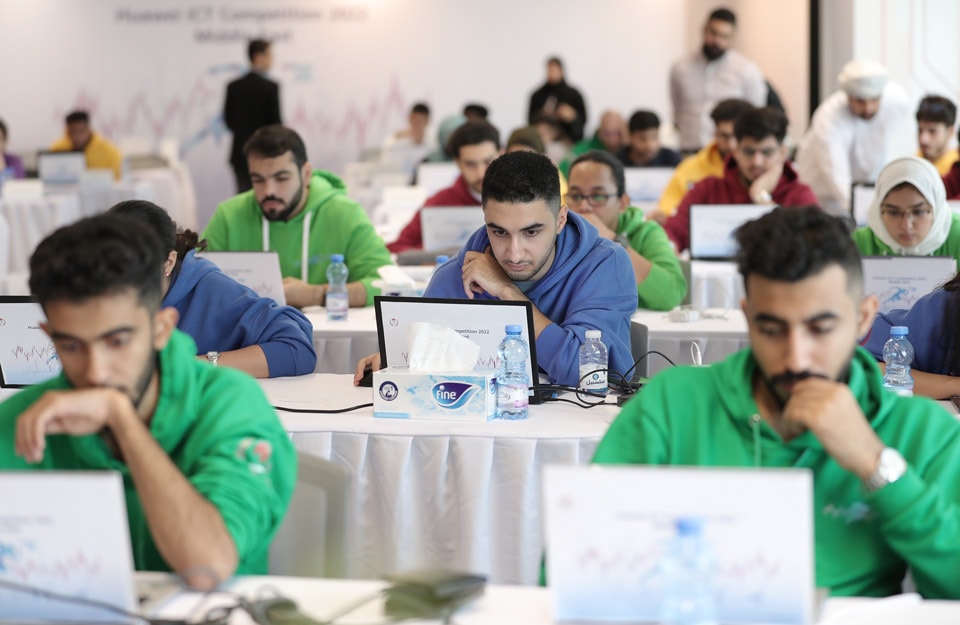
As an innovative ICT company, Huawei is well aware of the importance of talent cultivation and is committed to sharing its years of industry expertise. In 2013, we launched the Huawei ICT Academy program, which brings the latest ICT knowledge and skills to universities and colleges to prepare students for the future needs of industries. By September 2023, we had partnered with over 2,600 universities around the world to establish Huawei ICT Academies, training more than 200,000 students in over 100 countries and regions every year.
In Tunisia, Huawei has established 68 ICT Academies and trained over 8,000 ICT students, for which it received the Republic of Tunisia's Prime Minister Medal. In Thailand, Huawei was awarded the Prime Minister's Best of Contributor in Human Capital Development Award for its efforts in training digital talent and supporting the country's digital economy. In China, Huawei has established more than 600 ICT Academies in partnership with universities. For example, the collaboration between Huawei and Shanghai Jiao Tong University has produced a talent training model that integrates courses, competitions, and entrepreneurship. Over a dozen training courses covering subjects such as IoT and AI can help students develop innovation skills and create startups. Over 2,000 outstanding students have been trained through this program.
The Huawei ICT Academy program supports universities and colleges in curricula development, faculty training, talent development, teaching transformation, and entrepreneurship. It also helps match recruiters with graduates through ICT Talent Alliance job fairs, streamlining the last mile to employment.
Huawei is continuing to enrich the ICT Academy program. By establishing Huawei ICT Academy Support Centers (IASCs) worldwide, releasing the ICT Academy Growth Index, and launching the School Seeds Program, we help all ICT Academies grow and facilitate digital inclusion around the world.
Huawei will bring ICT education resources to more universities and colleges around the world. We plan to establish Huawei ICT Academies in partnership with over 6,000 schools by 2026 to train more than one million students annually.
By developing more ICT talent with digital skills, we aim to accelerate industry transformation and create a more intelligent future.
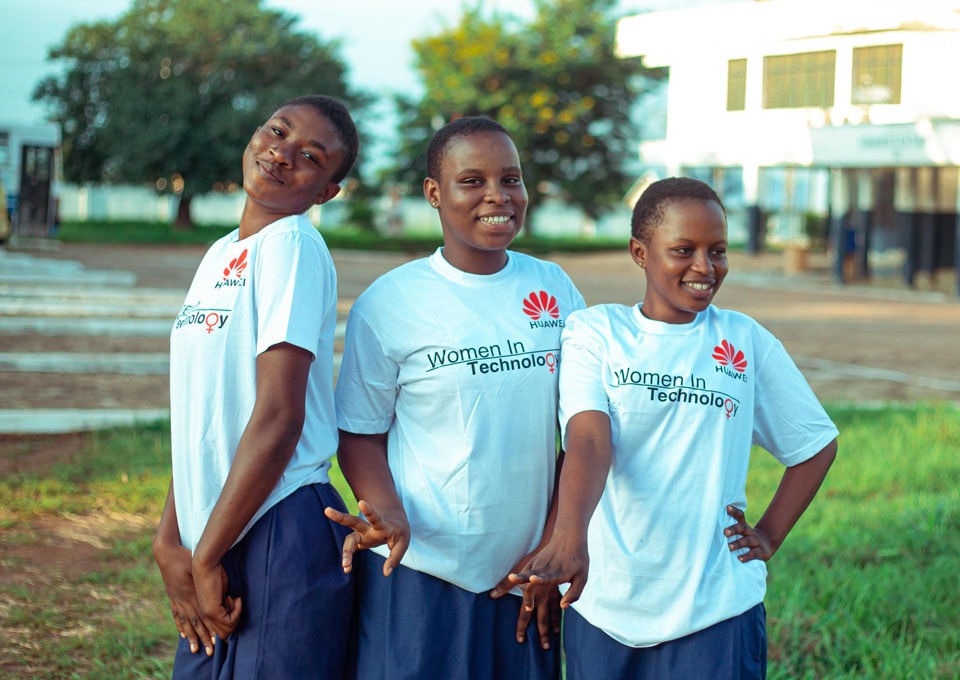
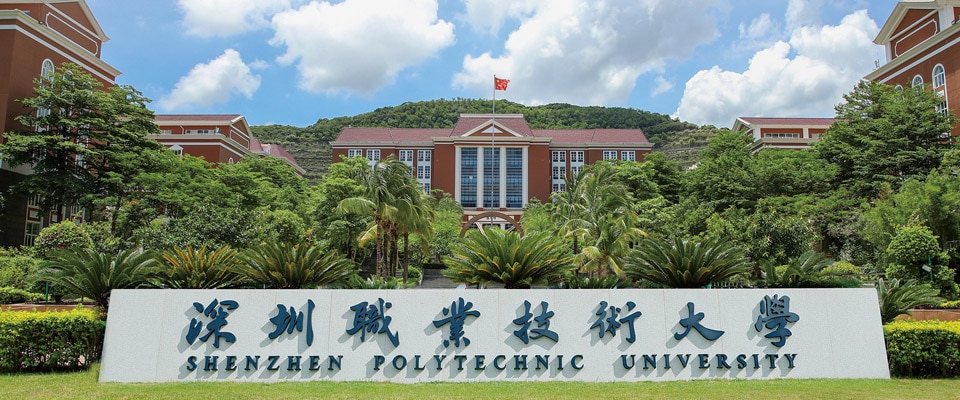































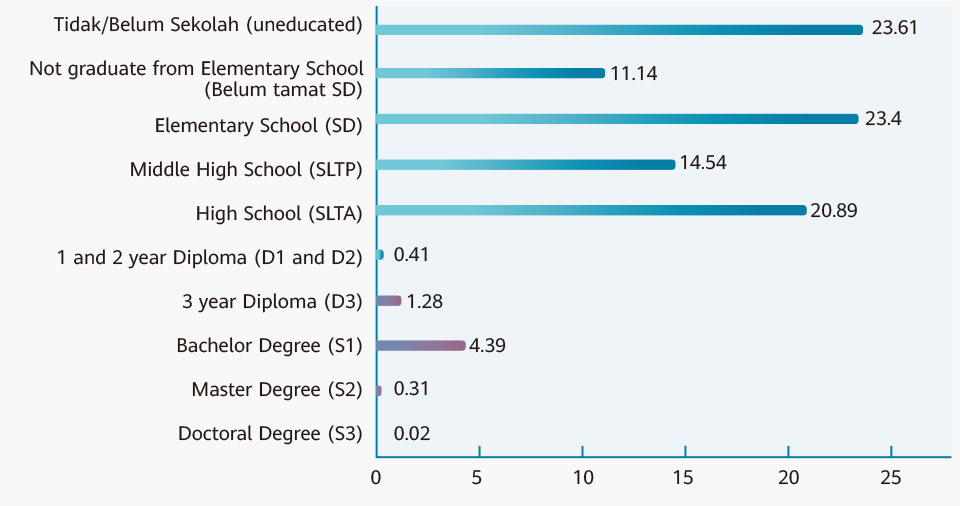
















Huawei has demonstrated how enterprises play an important role in accelerating progress towards SDG 4 by facilitating the creation of quality education and promoting lifelong learning opportunities.